In todays session we will see some of the most important data types in Python and some Examples...
In previous examples we have seen how to use print ,If we are using python3 then print is a function, syntax is as follows.
print (arguments)
Let us see how to print in different ways.
Now let us see how to scan an input from user
ie to scan in string format:
variable=raw_input(arguments)
in python 3 raw_input is not available
to scan in integer format type cast it in python:
variable=int(raw_input(arguments)) or variable=input(arguments)
to print data type use print type(variable)
in python3 input function will read like string if not used the typecasting.
- ASSIGNMENT
Ans:
If we dont know a perticular function duty use help(function)
THANK YOU..
help(int),help(str)......
OPERATORS
ARITHMATIC
OPERATORS
+
(Addition)
-
(Subtraction)
*
(Multiplication)
/
(Division)
**
(Power of)
//
(Floor Division) -for removing decimal part after division
RELATIONAL
OPERATORS
<
(Less
than)
>
(Greater than)
=
(Assignment)
!=
(Not Equal to)
==
(Comparison)
<=
(Less than or equal to)
>=
(greater than or equal to)
LOGICAL
OPERATORS
and
- logical anding
or
- logical
oring
not
- logical Noting
BITWISE
OPERATORS
&
(And)
|
(Or)
~
(Complement)
<<
(Left shift)
>>
(Right shift)
Python is very efficient in memory saving.every thing is treated as seperate object but we get same address for x and z also for y and k since their value is same.Every memory is allocated dynamically.
to find size of an object use : variable.__sizeof__()
MEMBERSHIP
OPERATORS
in
, not in
In a list ie:-
l=[10,20,30,40]
10 in l will give true,10 not in l will give False
IDENTITY
OPERATORS
is
,is not
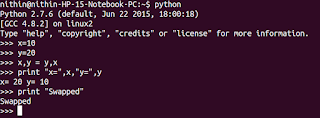
x=10
y=20
x is not y => True
x is y=> False
In the next sections we will see more about Data Types in Python...THANK YOU..























Thnk you for this info
ReplyDeleteHope you got something from it..😊
DeleteThank You.