I²C (Inter-Integrated Circuit), pronounced I-squared-C or I-two-C, is a multi-master, multi-slave, packet switched, single-ended, serial computer bus invented by Philips Semiconductor (now NXP Semiconductors). It is typically used for attaching lower-speed peripheral ICs to processors and microcontrollers in short-distance, intra-board communication. Alternatively I²C is spelled I2C (pronounced I-two-C) or IIC (pronounced I-I-C).
Since October 10, 2006, no licensing fees are required to implement the I²C protocol. However, fees are required to obtain I²C slave addresses allocated by NXP.
Several competitors, such as Siemens AG (later Infineon Technologies AG, now Intel mobile communications), NEC, Texas Instruments, STMicroelectronics (formerly SGS-Thomson), Motorola (later Freescale, now merged with NXP), Nordic Semiconductor and Intersil, have introduced compatible I²C products to the market since the mid-1990s.
SMBus, defined by Intel in 1995, is a subset of I²C, defining a stricter usage. One purpose of SMBus is to promote robustness and interoperability. Accordingly, modern I²C systems incorporate some policies and rules from SMBus, sometimes supporting both I²C and SMBus, requiring only minimal reconfiguration either by commanding or output pin use.
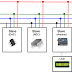
I2C requires only two wires connecting all peripherals to microcontroller.I2C requires two wires SDA (serial data line) and SCL (serial clock line) to carry information between devices. It is a master to slave communication protocol. Each slave has a unique address. Master device sends the address of the target slave device and read/write flag. The address is match any slave device that device is ON, remaining slave devices are disable mode. Once the address is match communication proceed between master and that slave device and transmitting and receiving the data. The transmitter send 8-bit data, the receiver replies 1-bit of acknowledgement. When the communication is completed master issues the stop condition. The I2C bus was developed by Philips Semiconductors. Its original purpose is providing an easy way to connect CPU to peripherals chips. Peripheral devices in embedded systems are often connected to the microcontroller as memory mapped devices. I2C requires only two wires for connecting all the peripherals to the microcontroller. These active wires, called SDA and SCL, are both bidirectional. SDA line is a serial data line and SCA line is a serial clock line.

I2C Pull-up Resistors:
Why given the pull-up resisters in I2C SCL and SDA line.
- Both SDA and SCL lines are open drain drivers.
- Its can be drive output low canot driver it high.
- For the lines to be able to go high you must provide pull-up resistors.















0 on: "I²C PROTOCOL"